"For every lock, there is someone trying to pick it, or break it." - David Bernstein
One of the biggest problems with traditional user ID and password login is the need to maintain a password database. Whether encrypted or not, if the database is captured, it provides an attacker with a source to verify their guesses at speeds limited only by their hardware resources. Given enough time, a captured password database will fall.
As processing speeds of CPUs increase, brute force attacks have become a real threat. GPGPU cracking can produce more than 500,000,000 passwords per second even on lower end gaming hardware. Depending on the software, it can take as little as 160 seconds to crack a 14-character alphanumeric password. A password database alone does not stand a chance against such methods when it is a real target of interest.
An MFA solution should be the floor that every organization utilizes in their Cyber Security posture. MFA increases the likelihood that an entity involved in communication or requesting access to a system is who, or what, they are declared to be.
What is MFA?
Multifactor authentication (MFA) is a security system that requires more than one method of authentication from independent categories of credentials to verify the user’s identity for a login or other transaction. Multifactor authentication combines two or more independent credentials: what the user knows as a “Password”, what the user has, a “Security Token” and/or what the user is “Biometric Verification”.
The goal of MFA is to create a layered defense and make it more difficult for an unauthorized person to access a target, such as a physical location, computing device, network, or database. If one factor is compromised or broken, the attacker still has at least one more barrier to breach before successfully breaking into the target. In the past, MFA systems typically relied upon two-factor authentication.
Why should organizations implement MFA?
Adding security should be an enabler of doing business and not a cost of doing business. The easiest way to achieve this is by using MFA.
MFA has three common categories:
- Knowledge factor – something you know (e.g., Name of your elementary school, PIN…)
- Possession factor – something you have (e.g., Key fob or Token…)
- Inherence factor – something you are (e.g., Biometrics, Retinal, Fingerprint, or Facial scan…)
Adding these layers to your security posture adds complexity and acts as a deterrent to bad actors.
Multi-factor authentication can help prevent some of the most common and successful types of cyberattacks, including automated credential stuffing, brute force and reverse brute force attacks and man-in-the-middle attacks. It also limits the impact of phishing, since a stolen or guessed password alone is insufficient for a hacker to gain access.
“Based on our studies, your account is more than 99.9% less likely to be compromised if you use MFA” - Alex Weinert, Group Program Manager for Identity Security & Protection, Microsoft
Is MFA Safe?
MFA hacking has existed since the 1990s via phishing network sessions. The real challenge is to ensure that the password recovery is not predictable “20% of password recovery questions are predictable, and the answers are readily available in the user’s social profiles.” (Source: darkreading.com).
If there is no way to customize the security questions, answer with unique responses.
Examples of this would be:
What is your Mother’s maiden name?
ManchesterUnited#1
What was our first car?
ManchesterUnited#1
What school did you first attend?
ManchesterUnited#1
The key is to make the response unpredictable and unique.
Which MFA solution to use?
There are a lot of MFA solutions in the market and there is no correct answer to this question. When it comes to MFA technology, it is important to determine which deployment methods and 2nd factors will best suite your organization needs and budget. Like any security tool, if the solution adds complexity to the end users, then that solution will not be widely adopted.
This chart outlines some examples with strengths, weaknesses, and cost comparatives. It is clear that enterprises must continue to evolve and improve their authentication of users, moving beyond the limitations of passwords.
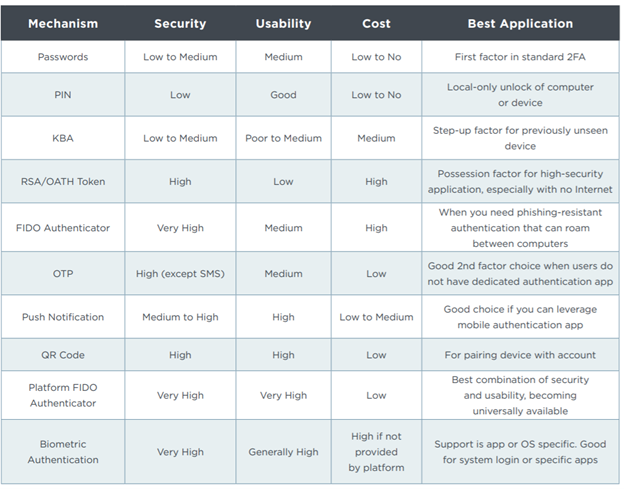
Ping Identity”, Multi-factor Authentication: Best Practices for Securing the Modern Digital Enterprise,” September 2020,
"People often represent the weakest link in the security chain and are chronically responsible for the failure of security systems." Bruce Schneier Cyber Security expert.
In conclusion, having an MFA solution should be a critical component in every organization’s security posture. It should also include a robust XDR solution layered with an external MDR solution. The challenge is selecting a solution that can be policy driven and adoptive but not adding complexity at the expense of productivity. Google research found that multi-factor authentication is extremely effective in preventing any attack that involves a bad actor obtaining or guessing the user's credentials.
Furthermore, MFA via on-device prompts blocks 99% of bulk phishing attacks and 90% of targeted attacks. Human factor should be considered when selecting any MFA solution. To learn more about how your organization can adopt an MFA strategy, please reach out to us to start a conversation.